Share:
This article concentrates on the process of commercial judgment enforcement in Vietnam.
At the end of a commercial dispute at a court or arbitration in Vietnam, a judgment or arbitral award with legal effect (the “Judgment“)[1], must be performed by the judgment debtor. However, in many cases, the Judgment debtor does not voluntarily perform his/her obligations, making the Judgment unenforceable. In this article, we would like to share our legal experience and guidance on Judgment enforcement in Vietnam.
1. Request for Judgment enforcement
1.1 Statute of limitations for requesting Judgment enforcement
Pursuant to the Law on Enforcement of civil judgments No. 26/2008/QH12 which was amended and supplemented by Law No. 64/2014/QH13 (the “LOECJ”), the statute of limitation for requesting Judgment enforcement is 05 years from the date on which the Judgment took effect. If a time limit for fulfilling an obligation is set in the Judgment, the 5-year statute of limitations shall commence from the date the obligation is due. For Judgments subject to periodical enforcement, the 5-year statute of limitations shall apply to each period and commence from the date the obligation is due.
Cases that are not included in the statute of limitations for Judgment enforcement, include (i) Time to postpone or suspend Judgment enforcement, except for the case of the Judgment creditor allowing the Judgment debtor to postpone the Judgment enforcement; (ii) Time occurring an objective obstacle or a force majeure circumstance that prevents the Judgment enforcement request on time if there are proven grounds.
The Judgment enforcement requester should note the above regulations on the statute of limitations so as not to lose this right due to the expiration of the statute of limitations. This note may also help to ensure their legitimate rights and interests in case the Judgment debtor intentionally delays their obligation performance.
1.2 Preparation of a petition for Judgment enforcement
The form and contents of the petition for Judgment enforcement must comply with the regulations of the applicable law. Accordingly, the petitioner can draft a petition for Judgment enforcement that meets the form and contents specified in Article 31 of the LOECJ or use Form No. D 04-THADS (attached with Circular No. 01/2016/TT-BTP dated 01 February 2016 issued by the Ministry of Justice).
When drafting the petition, the Judgment enforcement requester should accurately determine the competent civil judgment enforcement agency (the “EA”) under the law to avoid the case where the request for Judgment enforcement is refused, which prolongs the case settlement process.
In case the Judgment enforcement requester authorizes another person to draft and submit the petition for Judgment enforcement, the petition must entirely present the authorized party’s information and be attached with a power of attorney.
The Judgment enforcement requester has to send the Judgment that they requested for enforcement and other relevant documents (if any) attached to the petition for Judgment enforcement to prove their request.
2. Time limit for Judgment enforcement
Applicable law does not specify the maximum period for enforcement of a Judgment. The speed and effectiveness of Judgment enforcement rely upon numerous elements particular to each case.
Judgments are usually enforced more quickly if the Judgment debtor voluntarily submits the money or assets; if the Judgment creditor and Judgment debtor can reach an agreement on Judgment enforcement; or if a Judgment debtor’s assets are purchased immediately after being seized. If these conditions do not exist, Judgments may take longer to be enforced and it may last indefinite.
In some cases, because of the violation from the Judgment debtor or the EA, the Judgment enforcement period has been extended.
Some examples are Judgment debtors purposefully filing complaints or denouncements to obstruct the Judgment enforcement process or when the EA violates procedures for organizing Judgment enforcement (such as failing to notify and serve Judgment enforcement decisions/notices in time, to conduct the verification/ periodic verification, or being slow to take action after verification results are available, etc.).
3. Guidance to speed up the enforcement Judgment process
As mentioned in section 2, we could see that due to many reasons, the Judgment enforcement period can take indefinitely. To speed up this process, here are some guidance points to note when participating in Judgment enforcement:
3.1 Understanding partner’s position
Parties should understand each other’s operations, processes, and business efficiency as well as the financial ability of the partner to comply with and satisfy a Judgment enforcement action if necessary, right from the beginning when signing a commercial contract.
3.2 Support the EA in the process of Judgment enforcement
The Judgment creditor must actively gather information about conditions for Judgment enforcement of the Judgment debtor.
When there exist details about the assets of the Judgment debtor, the Judgment creditor needs to promptly ask the EA to implement measures in order to prevent the judgment debtor from changing the property’s status, dispersing or destroying property, or evading their judgment enforcement obligations.
3.3 Supervision to ensure that the judgment enforcement process complies with the law
The Judgment creditor should actively monitor, contact, and request the EA to issue the decision, notice, and response as well as make any necessary procedures to enforce Judgment on time. If violations occur when processing Judgment enforcement, such as violating the time limit for verifying the conditions for Judgment enforcement, being slow to perform coercive Judgment enforcement, etc., the Judgment creditor needs to file a written complaint and report it promptly to the Heads of the EA and the Procuracies of the same level to direct the EA to remedy the violations and organize the Judgment enforcement in accordance with the law.
For complaints and denunciations from the Judgment debtor, the Judgment creditor needs to understand the law and make objections requesting the EA to quickly and completely settle the groundless complaint, thereby speeding up the Judgment enforcement process.
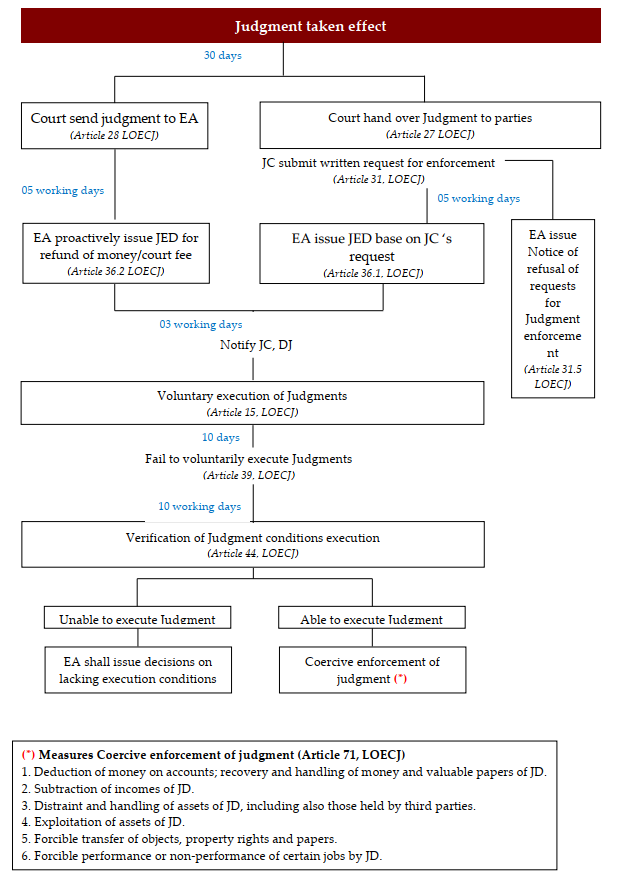
4. Judgment enforcement process
In general, the Judgment enforcement process is as follows:

[1] Judgment including judgments and decisions or parts of judgments and decisions of first-instance courts which have not been appealed or protested pursuant to appellate procedures; judgments and decisions of appellate courts; cassation or reopening of trial decisions by courts; awards and decisions of commercial arbitrations.

